DeMyelination And Axonal Degeneration In Multiple Sclerosis
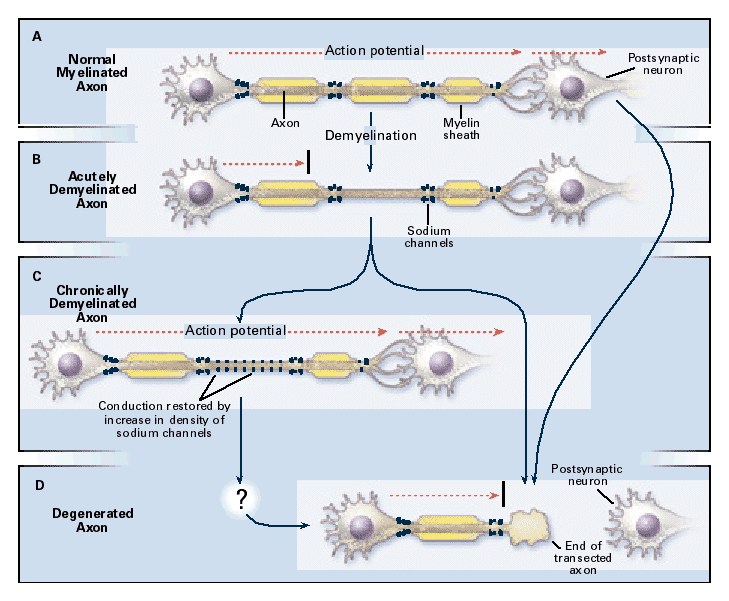 |
In Panel A: In Panel B: In Panel C: In Panel D: Copyright © 1998 by the Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved. |
 |
In Panel A: In Panel B: In Panel C: In Panel D: Copyright © 1998 by the Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved. |