Interferon-gamma (IFN-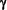 ) is implicated as a participant in the Immune Effector and Regulatory mechanisms considered to mediate the PathoGenesis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
) is implicated as a participant in the Immune Effector and Regulatory mechanisms considered to mediate the PathoGenesis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
We have used an IntraCellular Cytokine staining technique to demonstrate that the proportion of ex vivo peripheral blood CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell subsets expressing IFN-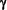 is increased in Secondary/Progressing (SP) MS patients.
is increased in Secondary/Progressing (SP) MS patients.
Whereas the values in untreated Relapsing/Remitting (RR) MS patients are reduced compared with those of controls. Patients treated with Interferon-ß (IFN-ß) have an even more significant reduction in the percentage of IFN-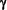 -secreting cells.
-secreting cells.
The finding that the number of IFN-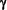 -expressing CD8+ Cells is increased in SPMS patients, a group with reduced functional Suppressor activity, and is most significantly reduced by IFN-ß therapy, which increases Suppressor activity, indicates that IFN-
-expressing CD8+ Cells is increased in SPMS patients, a group with reduced functional Suppressor activity, and is most significantly reduced by IFN-ß therapy, which increases Suppressor activity, indicates that IFN-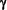 secretion by CD8+ T-Cells and functional Suppressor defects attributed to this cell subset in MS can be dissociated.
secretion by CD8+ T-Cells and functional Suppressor defects attributed to this cell subset in MS can be dissociated.