Objective
To determine the effects of combination all-trans Retinoic Acid (RA) and Interferon-ß-1b therapy on Immune System Functions, potentially relevant to Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
Design
Interferon 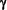 -secreting cells, T-Suppressor cell function, and Lymphocyte proliferative responses were assayed using peripheral blood MonoNuclear Cells from patients with MS and control subjects under control conditions and in the presence of Interferon-ß-1b, RA, and the two combined.
-secreting cells, T-Suppressor cell function, and Lymphocyte proliferative responses were assayed using peripheral blood MonoNuclear Cells from patients with MS and control subjects under control conditions and in the presence of Interferon-ß-1b, RA, and the two combined.
Participants
Seventeen patients with Secondary/Progressive MS and 25 control subjects in a university hospital MS Clinic.
Results
Interferon-ß-1b use increased Interferon 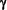 -secreting cell counts, augmented T-Suppressor cell function, and inhibited T-Cell proliferation.
-secreting cell counts, augmented T-Suppressor cell function, and inhibited T-Cell proliferation.
Therapy with RA decreased Interferon 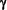 -secreting cell counts, had a minimal positive effect on T-Suppressor cell function, and had no effect on T-Cell proliferation.
-secreting cell counts, had a minimal positive effect on T-Suppressor cell function, and had no effect on T-Cell proliferation.
When RA and Interferon-ß-1b were combined, the inhibitory effect of RA on Interferon 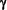 -secreting cells predominated, T-Suppressor cell function increased synergistically over the increment observed with Interferon-ß-1b use alone, and the inhibitory effect of Interferon-ß-1b alone on T-cell proliferation remained unchanged.
-secreting cells predominated, T-Suppressor cell function increased synergistically over the increment observed with Interferon-ß-1b use alone, and the inhibitory effect of Interferon-ß-1b alone on T-cell proliferation remained unchanged.
Conclusions
Treatment with Interferon-ß-1b partially restores defective T-Suppressor cell function in patients with MS. This potentially beneficial action is synergistically potentiated by RA.
Interferon-ß-1b increases the number of Interferon 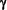 -secreting cells in the circulation when treatment is initiated.
-secreting cells in the circulation when treatment is initiated.
A similar increment in Interferon 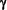 -secreting cells is observed when Interferon beta-1b is added to cultural peripheral blood Mononuclear cells in vitro. This potentially deleterious action of Interferon-ß-1b is reversed by RA.
-secreting cells is observed when Interferon beta-1b is added to cultural peripheral blood Mononuclear cells in vitro. This potentially deleterious action of Interferon-ß-1b is reversed by RA.
Interferon-ß-1b inhibits Lymphocyte proliferation modestly but reproducibly. This action of Interferon-ß-1b is unaltered by RA.
These data provide a rationale for a trial of combination treatment with Interferon-ß-1b and RA in patients with MS.