#2
Prevention Of EAE Via Inhibition Of IL-12 Signaling And IL-12-Mediated Th1 Differentiation: Effect Of The Anti-Inflammatory Drug Lisofylline
Bright JJ, Du C, Coon M, Sriram S, Klaus SJ
J Immunol 1998 Dec 15;161(12):7015-22
Vanderbilt Univ, Medical Center, Dept of Neurology, Nashville, TN 37212, USA
UI# 99077574
Abstract
Experimental Allergic EncephaloMyelitis (EAE) is an Inflammatory, CD4+ Th1-mediated AutoImmune Disease, which serves as a model for Multiple Sclerosis.
We examined the effect of a novel Anti-Inflammatory drug, Lisofylline (LSF), on EAE induced either by injection of mouse Spinal Cord homogenate or following transfer of Myelin Basic Protein-reactive T-Cells.
Orally administered LSF significantly inhibited EAE in both cases, decreasing peak clinical scores by >70% and >80%, respectively.
In addition, analysis of representative Spinal Cord sections from LSF-treated mice showed complete lack of DeMyelination and Lymphocyte infiltration.
The reduction in EAE correlated with the inhibition of Th1 differentiation by LSF in vivo, as indicated by a reduction in T-Cell IFN-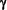 production ex vivo after Ag restimulation. production ex vivo after Ag restimulation.
The inhibition of Th1 differentiation in vivo is consistent with a block in IL-12 receptor signaling, because LSF blocked IL-12-driven Th1 differentiation and T-Cell proliferation in vitro, yet had no effect on IL-12 secretion from APCs ex vivo or in vitro.
#3
Pentoxifylline Is Not A Promising Treatment For Multiple Sclerosis In Progression Phase
Myers LW, Ellison GW, Merrill JE, El Hajjar A, St Pierre B, Hijazin M, Leake BD, Bentson JR, Nuwer MR, Tourtellotte WW, Davis P, Granger D, Fahey JL
Neurology 1998 Nov;51(5):1483-6
UCLA School of Medicine, Dept of Neurology, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1769, USA
UI# 99034200
Abstract
Fourteen MS patients took Pentoxifylline at varying doses for up to 24 months. In vitro production of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha was reduced in patients taking 2,400 to 3,200 mg/day of Pentoxifylline for 12 weeks or more.
Twelve of the 14 patients experienced worsening of the disease during the study according to clinical, MRI, or Visual Evoked Potential criteria. These results provide no hint of efficacy for Pentoxifylline as a treatment for MS in Progression phase.
#4
Controlled Therapeutic Trials Of Pentoxifylline In Relapsing-Experimental AutoImmune EncephaloMyelitis
Grassin M, Brochet B, Coussemacq M, Brochet H
Acta Neurol Scand 1998 Jun;97(6):404-8
Experimental NeuroBiology and Neuroimagery Laboratory, JE 480, BP 78, Universite Bordeaux II, France
UI# 98332138
Abstract
This study was designed to assess the capacity of several doses of Pentoxifylline to prevent or treat Chronic-Relapsing-EAE (CR-EAE) exacerbations induced in the Lewis rat.
Pentoxifylline (PTX) is a Methylxanthine derivative that inhibits the production of TNF- , a Cytokine involved in EAE and Multiple Sclerosis PhysioPathology. , a Cytokine involved in EAE and Multiple Sclerosis PhysioPathology.
Three blind placebo-controlled randomized studies were performed in respectively 40, 30 and 18 rats: a trial of different (PTX) dosages (8, 30, 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg) versus placebo to prevent EAE onset.
A trial of PTX (8, 30 or 50 mg/kg) versus placebo to prevent 2 attacks of EAE and a trial of PTX (100 mg/kg) versus placebo to abrogate ongoing clinical EAE.
No statistically significant difference was observed between groups in any trial. PTX was ineffective to prevent or treat CR-EAE in these studies.
#5
Liedtke W, Cannella B, Mazzaccaro RJ, Clements JM, Miller KM, Wucherpfennig KW, Gearing AJ, Raine CS
Ann Neurol 1998 Jul;44(1):35-46
Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Dept of Pathology, Bronx, NY, USA
UI# 98330165
Abstract
The ProInflammatory Th1 Cytokine, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF- ), the cell death signaling molecule FasL, and several ExtraCellular Matrix degrading MetalloProteinases have been implicated in the PathoGenesis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). ), the cell death signaling molecule FasL, and several ExtraCellular Matrix degrading MetalloProteinases have been implicated in the PathoGenesis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
The latter enzymes, as well as TNF- converting enzyme and FasL-converting enzyme, can be blocked by Matrix MetalloProteinase Inhibitors (MMPIs). converting enzyme and FasL-converting enzyme, can be blocked by Matrix MetalloProteinase Inhibitors (MMPIs).
In this study, we show that a potent MMPI was clinically effective in an animal model for MS, Experimental AutoImmune EncephaloMyelitis (EAE) in the SJL/J mouse.
Efficacy was remarkable, as indicated by blocking and reversal of acute disease and reduced number of relapses and diminished mean cumulative disease score in Chronic Relapsing animals.
Also, DeMyelination and Glial scarring were significantly decreased in MMPI-treated mice with chronic Relapsing EAE, as was Central Nervous System Gene expression for TNF- and fasL. and fasL.
It is interesting that expression of the beneficial Cytokine InterLeukin-4 (IL-4) was increased, and IL-4 was expressed on Glial Cells.
The relevance of these compounds for MS was underscored by their ability to specifically inhibit TNF- shedding and CytoToxicity of Myelin-AutoReactive human Cytotoxic CD4+ T-Cell clones. shedding and CytoToxicity of Myelin-AutoReactive human Cytotoxic CD4+ T-Cell clones.
This is the first report to show a positive effect by MMPIs on Chronic Relapsing EAE, its Central Nervous System Cytokine profile, and on TNF- shedding by human Myelin-AutoReactive T-Cells. shedding by human Myelin-AutoReactive T-Cells. |